Why does Enterprise File Security matter to organisations?
In today’s business landscape, enterprise risk management (ERM) is more important than ever. With the increasing amount of data that organisations collect and store, the risk of data breaches and other security threats is a rising concern. That’s why effective enterprise file security is essential for any organisation that wants to safeguard its valuable data and protect its reputation.
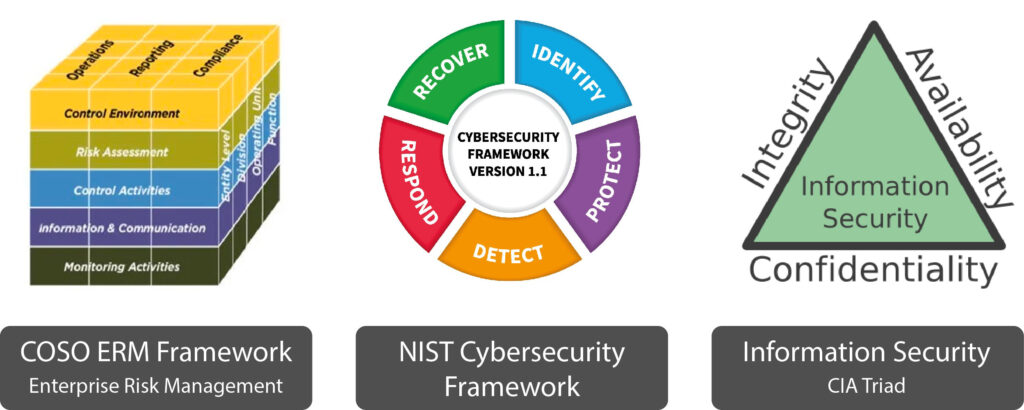
Most of the CIOs and IT Directors are more familiar with the following: COSO ERM Framework, NIST Cybersecurity Framework and CIA Triad. Here is how we are drawing from these established guidelines and best practices to apply them for protecting data in file exchanges.
1. COSO ERM Framework
This framework is used by thousands of enterprises worldwide to enhance their internal controls, providing a more extensive and robust focus on the area of Enterprise Risk Management. Not only does it concentrate on broader strategic objectives but also company culture and concepts such as risk appetite.
There are 5 components in COSO ERM Framework:
1. Risk Governance and Culture: This involves establishing a risk governance structure and promoting a risk-aware culture within the organization.
2. Risk Assessment: This involves identifying and analysing risks that may affect the organisation’s objectives.
3. Risk Response: This involves developing and implementing risk responses to address identified risks.
4. Information, Communication and Reporting: This involves establishing processes for collecting, analysing and communicating risk related information across the organisation.
5. Monitoring and Review: This involves establishing processes for monitoring and reviewing the effectiveness of the organisation’s risks management activities.To manage Enterprise Risks effectively, businesses should establish an ERM program and risk management policy, identify and assess risks, develop risk response plans, and continuously monitor and review their risk management processes.
This framework can be effectively applied to manage risks associated with file security and exchanges. It can be used to set clear objectives for data security and identify potential risks (such as data breaches and unauthorised access) and establish robust data protection measures.
2. NIST Cybersecurity Framework
This framework was developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to provide organizations with a comprehensive approach to managing and reducing cybersecurity risk.
There are 5 components in NIST Cybersecurity Framework: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, Recover
When it comes to file security, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework can be applied in the following ways:
Identify: Identify and understand the types of data that need to be protected, the systems and processes that handle the data, and the potential risks to those systems and processes. This could involve classifying of all sensitive files, identifying their criticality, and assessing their risk exposure.
Protect: Implement safeguards to protect sensitive files and exchanges from unauthorised access or theft. This could involve implementing access controls, encryption, data classification, virus scanning and other security measures to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the files.
Detect: Integrate with monitoring mechanisms to detect security breaches and other security incidents. This could involve setting up security alerts and conducting regular security audits to identify potential security threats.
Respond: Create an incident response plan to respond to security breaches and other security incidents. This could involve developing a detailed response plan outlining the actions to be taken in the event of a security breach, such as notifying affected parties, conducting forensic investigations, and restoring affected systems and processes.
Recover: Prepare a plan for recovering from security breaches and other security incidents. This could involve restoring files and processes to their pre-incident state, conducting post-incident reviews, and implementing changes to prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future.
3. CIA Triad for Information Security
More specifically for digital assets, there is also the CIA triad for Information Security guiding us. The CIA triad consists of three main components: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability.
Confidentiality: The assurance that sensitive information is only accessed by authoriszed individuals or entities. It’s about keeping information private and secure. Confidentiality can be achieved through measures such as files encryption, granular access controls, and secure storage.
Integrity: The accuracy and completeness of information. It ensures that data has not been tampered with, altered or destroyed in an unauthorised manner. Maintaining data integrity requires implementing measures such as immutable backups, version controls, data validation, and access controls.
Availability: The ability of authorised users to access information and resources when they need it. Availability can be threatened by events such as natural disasters, system failures, or denial-of-service attacks. To ensure availability, it is important to have redundancy, backups, and disaster recovery plans in place.
By applying the CIA triad, organisations can ensure that critical files are protected from unauthorised access, modifications, and loss, while also ensuring that authorised individuals have access to the data when needed.
Enterprise File Security Matters!
From the above, it is imperative that organisations should regularly identify and mitigate the risks of data breaches and other security threats through implementing effective file security measures.
While implementing file security measures, organisations can leverage on readily available Enterprise File Security platforms such as EasiShare to secure, manage and govern files while ensuring end users and IT operational team remain productive. It empowers them to take back control on how to secure their digital assets & decide where their data resides. Some security measures that organisations can achieve includes:
Access controls: Implementing access controls and further secure user authentication with 2FA, to ensure that only authorised users can access sensitive files.
Anti-virus/CDR: To detect and remove malwares
Encryption: Encrypting files at rest and in transit to protect them from unauthorized access or disclosure.
Data Backups: Regularly backing up data to ensure that it can be recovered in the event of a data loss. Have backup approaches that can meet the RTO/RPO for business.
Monitoring and Logging: Implementing monitoring and logging tools to detect, proactively pre-empt and respond to security incidents.
Through the use of EasiShare, organisations can better stay on track to achieve their goals with Digital Workplace Governance, Cyber Resilience, and Data Sovereignty Compliance.




